How To Prevent Injuries While Cycling

Cycling is a great way to stay active, enjoy the outdoors, and explore new places. However, it can also be a risky activity if you’re not careful.
Injuries are all too common, from scrapes and bruises to more serious accidents that can require hospitalization.
If you’re an avid cyclist, or just starting out, it’s important to take steps to prevent injury and stay safe on the road.
In this article, we’ll explore some of the best ways to prevent injury while cycling, from basic safety gear to proper technique and training.
Whether you’re a casual rider or a seasoned pro, these tips will help you stay healthy and enjoy your time on the bike.
Common Cycling Injuries And Preventions
Some of the most common cycling injuries include head injuries, neck and back pain, wrist and forearm pain, knee pain, cyclist’s knee (Patellofemoral pain syndrome, PFPS), lateral hip pain, Achilles and Patella Tendinitis, saddle sores, numb butts, genital problems, road rash, and broken bones.
While these injuries may seem daunting, there are steps you can take to prevent them.
Let’s dive in.
Head Injury
Bicycle-related crashes often result in head injuries, which account for 60% of deaths and 30% of emergency department visits. The most effective way to prevent a head injury while cycling is to wear a specialized cycling helmet (not other kind of helmet). Helmets protect the head and reduce head injury by 80%, but few riders wear them. (1)
In addition to wearing a helmet, it’s also wise to select the right bike and accessories to minimize the risk of a head injury.
Bikes with a lower center of gravity and wide tires can provide greater stability, while handlebar height and seat position can be adjusted to improve posture and reduce strain on the neck.
Despite taking precautions, accidents can still happen. In that case, it is important to seek emergency medical attention as soon as possible.
Neck & Back Pain
One of the most important things you can do to prevent neck pain and back pain is to maintain proper posture while cycling. (2)
This means tightening your abs, elongating your torso, dropping your shoulders, keeping your chest lifted, and slightly tucking your chin.
These adjustments help to ensure that your spine stays in a neutral position, which minimizes stress on your neck and back.

Stretching your neck and shoulders regularly is another effective way to prevent pain while cycling.
Before and after a ride, take a few minutes to stretch your neck by gently tilting your head back and forth and side to side. You can also stretch your shoulders by doing arm circles and shoulder rolls.
If you’re experiencing neck pain and back pain while cycling, consider cross-training to strengthen your core. By doing exercises like planks and sit-ups, you can build up the muscles that support your spine.
Wrist & Forearm Pain
There could be multiple reasons behind wrist and forearm pain, such as putting too much weight on your palms, incorrect forearm posture, or even a bike fit that’s not suitable for you. (3)
To avoid such discomfort, the first step is to ensure that your handlebars are correctly adjusted.
This will allow for a slight bend in your elbows and flexible wrists, reducing the stress on your wrists and forearms.
Another essential aspect to keep in mind is the position of your head and spine. Proper alignment of these will reduce the possibility of hand pain.
To further cushion your hands and wrists, you can always invest in gel gloves or padded bar tape. These accessories offer extra padding in critical areas, thereby reducing the stress on your palms and wrists.
Last but not least, make sure your saddle is parallel to the ground to prevent any increase in wrist and hand discomfort.
Knee Pain
Medial and lateral pains on the sides of the knee are common types of knee pain among cyclists. One of the most common reasons for this type of pain is incorrect cleat setup.
This can lead to additional stress on the knees, causing pain. Adjusting the cleats’ position is essential to prevent this type of pain.
Pain behind the knee is another type of knee pain that cyclists may experience, and it is commonly a result of a saddle that is too high. When pedaling, the leg will overextend, leading to added stress on the knee and discomfort.

Lowering the saddle to the appropriate height will help prevent this type of pain.
In contrast, the anterior knee, which is located in the front of the knee, can be the cause of different types of knee pain.
It is often due to an improper bike fit or overuse. An improper bike fit could mean a saddle that is too far forward or too low, leading to an excessive strain on the knee joint. (4)
Overuse, on the other hand, happens when you increase the length, frequency, or intensity of your rides without gradually conditioning your body.
A sudden increase in exercise can cause excessive strain on the knee joints, leading to inflammation and pain.
Cyclist’s Knee (Patellofemoral pain syndrome, PFPS)
Cyclist’s Knee, also known as Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), is a common injury among cyclists that affects the kneecap.
It can cause discomfort and pain during activity or even during rest. This injury can be easily prevented by taking proper preventative measures.
One effective tip that can prevent Cyclist’s Knee is to keep the supporting muscles supple, especially the quads.

Stretching out your hips and glutes with a reclining pigeon pose will help to loosen tight muscles around the knee joint.
Engaging in strengthening exercises for your quads and glutes can also help prevent Cyclist’s Knee.
Building strength in these muscles through exercises such as squatting, lunging, and leg press can help reduce the strain on the knee joint during cycling. (5)
Lateral Hip Pain
Lateral hip pain is a common complaint among cyclists and refers to discomfort or pain on the outside of the hip.
It can range from a dull ache to sharp pain and can also result in a limited range of motion in the hip joint.
Cycling can contribute to lateral hip pain due to repetitive motion and prolonged periods of sitting on the bike.
Improper bike fit, weak hip flexors, rotators, and stabilizers, and tight muscles can also contribute to the development of lateral hip pain.

To alleviate lateral hip pain, it is important to keep the hip flexors, rotators, and stabilizers mobile.
Specific exercises such as the figure-4 trigger point and kneeling lunge can help stretch and strengthen these muscles, increasing their flexibility and range of motion.
In addition to stretching and exercise, trigger point release with a lacrosse ball can also be beneficial in alleviating lateral hip pain.
Achilles and Patella Tendinitis
Achilles and Patella Tendinitis are caused by overuse and improper bike fit. These conditions can result in discomfort, pain, and inflammation in the ankle and knee joints, respectively. (6)
The Achilles tendon is a long, thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the calf muscles. Constant flexing of this tendon during cycling can lead to inflammation and pain.
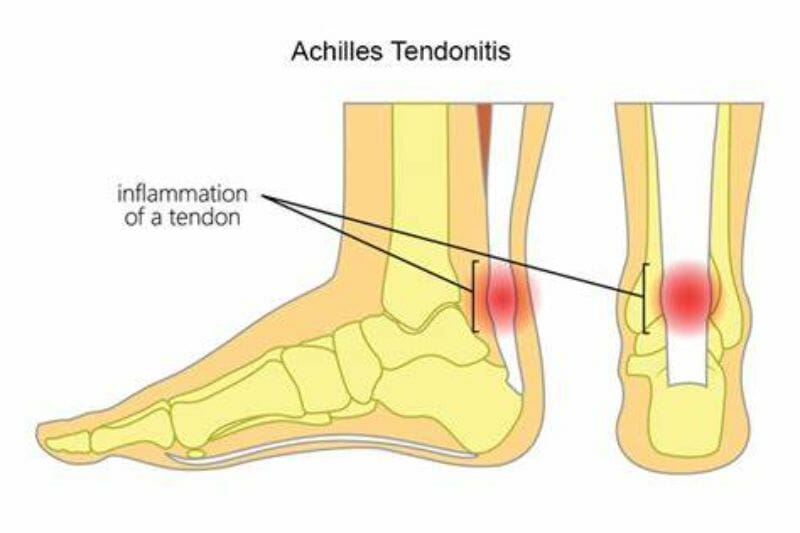
Proper shoe cleat position allows for a proper extension of the leg, avoiding excessive flexion of the Achilles tendon and reducing the risk of injury.
Managing Achilles or Patella Tendinitis involves various steps:
- Apply ice to the affected area to fight inflammation and reduce pain, especially after a training session.
- Take a break from cycling to allow the inflamed tendon to heal.
- Inserts for shoes or custom orthotics to reduce pressure on the affected tendon.
- Stretch the Achilles tendon regularly to improve its flexibility.
- Avoid dropping the heel too much when pedaling to prevent excessive stress on the tendon.
Saddle Sores
Saddle sores are a very common complaint among cyclists. These are painful, irritated, and often red bumps that occur on the skin around the buttocks and genital area due to prolonged friction caused by contact with the saddle.
They can lead to discomfort, pain, and even infection, and if left untreated, can lead to more serious health issues.
The key to preventing saddle sores is to keep the affected area clean and dry. You don’t want this vital area to become the source of bacteria which may lead to a jock itch.
To learn more about how to treat and prevent saddle sores, check out our article.

Choosing the appropriate saddle for your body type is also crucial. An ill-fitting saddle can cause unnecessary friction, leading to saddle sores.
Wearing well-fitting cycling shorts with proper chamois can also help reduce the risk of developing saddle sores.
Avoiding hair removal in the affected area can also help reduce friction and the risk of developing saddle sores.
In addition to these preventive measures, using chamois cream can kill off bacteria and reduce friction between the skin and saddle, reducing the risk of saddle sores.
While most saddle sores can be treated at home, stubborn ones can lead to more serious infections that require medical attention. Prompt medical care can help avoid further complications and discomfort.
Numb Butts
Numb butts occur when the perineal area’s nerves are compressed for an extended period, leading to numbness, discomfort, and even pain.
The first step in preventing numb butts while cycling is to ensure that your bike seat is positioned correctly with the initial setup. If the seat is too high or low, it can create pressure points and cause discomfort or numbness.
You want to make sure your sit bones find the cushion space on your bike seat to distribute your body’s weight evenly.
If the problem persists, you can try adding a padded seat cover to your bike seat. Padded seat covers can help distribute your weight evenly, reduce pressure on sensitive areas, and improve overall comfort while cycling.

However, keep in mind that it may take time to adapt to the pressure in that area, so don’t get discouraged if you experience mild discomfort initially. The goal is to build endurance while breaking in that tissue gently.
As you get accustomed to the ergonomics of the seat and your cycling regimen, you will notice that you can go for more extended periods without experiencing numbness and discomfort.
Genital Problems
Tight seating over a long period can cause incredible pain and discomfort in the genital regions. This problem is caused by a build-up of pressure in the blood vessels leading to those areas. (7)
For ladies, you know the struggle of chafing, saddle sores, and skin sensitivity all too well, not to mention the discomfort of labial enlargement, vaginal irritation, and infections.
For you gentlemen, you’re not off the hook either – genital numbness, erectile dysfunction, and painful ejaculation can all be issues for you (check out our article about how to secure your balls while cycling).
To avoid this problem, it’s essential to take measures that promote healthy blood flow to the area.
Wearing loose clothing, sitting on padded seats, and constantly changing positions while riding can significantly reduce the risk of genital pain and discomfort.
I’m a big fan of padded seat covers as they are an excellent option for providing additional cushioning and unparalleled comfort.
They can help ensure that your weight is evenly distributed across the seating area rather than resting solely on the genital region.
Moreover, it’s crucial to build up cycling gradually, allowing the body to adapt to the seated position. Starting with shorter rides of 15-20 minutes, and then increasing slowly from there.
Road Rash
Road rash is a result of skin abrasion due to a fall or accident on the road when the skin scrapes against the surface.
Road rash injuries can range from mild to severe, depending on the seriousness of the fall.
The first step to treating it is to wash your hands thoroughly. This is essential to avoid any infections while cleaning the wound.
Then, with clean water and mild soap, gently wash the injured area. Remove all dirt, grit, or gravel from the abrasion. You can also use a sterile saline solution or antiseptic wipes to clean the wound.
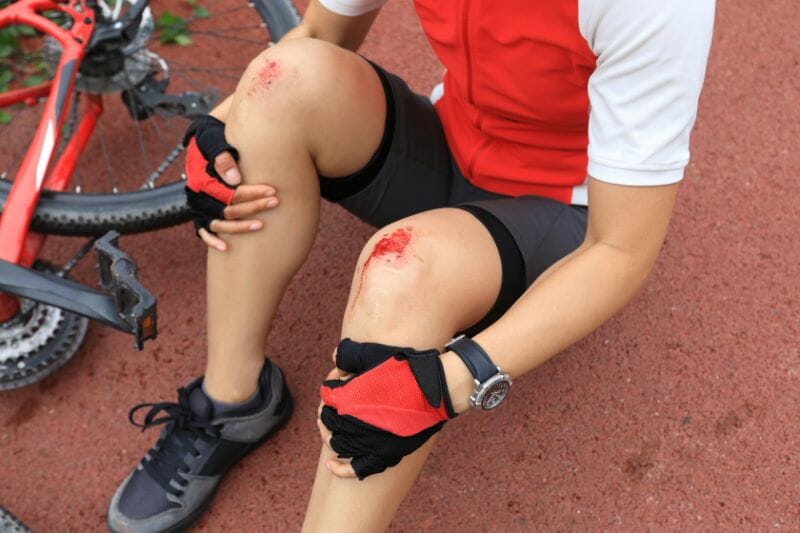

After removing all debris, dry the area gently with a clean towel. Apply a generous amount of antibiotic ointment to the wound to prevent any infections and promote healing.
Next, tightly bandage the wound. Use sterile gauze or a non-stick dressing to cover the wound. Secure it with adhesive tape, making sure it’s snug, but not too tight.
Road rash could be accompanied by other injuries such as broken bones or head trauma, depending on the fall’s severity. So if you feel any other pain, discomfort, or strange sensations, consider visiting a medical professional for further examinations.
Broken Bones
Broken bones are one of the most common and severe injuries that a cyclist can suffer from when involved in an accident.
Among the most frequent broken bones are the clavicle, wrist, ankle, and collarbone. These bones tend to break as a result of a high-impact fall, where pressure is placed on the bone upon hitting the ground.
To prevent broken bones while cycling, it is crucial to take measures to minimize injuries during a fall.

When in a sticky situation, try to minimize the impact by rolling instead of landing in one spot. This helps to reduce the force and pressure on specific bones, which can lead to breaks.
Another way to minimize the risk of breaking bones is by investing in protective gear. For instance, wearing a cycling helmet can go a long way in reducing head injuries, while padded gloves provide cushioning for the hands.
Other safety equipment such as elbow and knee pads can also help reduce the chances of breaking bones if there is an impact.
Remember that knee injuries can also lead to fractures. As such, it is crucial to exercise your knees regularly to build strength, enhance flexibility and reduce the chances of breaking a bone in case of an accident.
However, in the event of a fall resulting in broken bones, you should seek medical attention immediately to prevent further complications and hasten the healing process.
Additional Strategies To Prevent And Treat Cycling Injuries
Preventing and treating cycling injuries goes beyond just investing in safety gear and taking measures to minimize injuries in case of an accident.
Below, we’ll explore some easy tips to further reduce your risk of common injuries and improve your overall performance.
Improve Flexibility With Static Stretching
Static stretching is an essential activity for keeping your body flexible and reducing the risk of injury while cycling.
It involves holding a stretch for a period of time, typically 15-30 seconds, without bouncing or moving.

Here are five of the most relevant points to keep in mind when it comes to static stretching for cycling:
1. Work on your hip flexors to help improve posture. The hip flexors can become tight from prolonged periods of sitting and can cause an excessive forward tilt of the pelvis, leading to lower back pain and poor posture while cycling. A simple hip flexor stretch can help prevent this.
2. Focus on the calf muscles to reduce lower leg pain. Tight calf muscles can cause stiffness and pain in the lower legs while cycling. Consistent stretching of the calf muscles can help reduce pain and discomfort during rides.
3. Concentrate on your lower back and core for proper posture. Lower back pain is a common issue for cyclists. Stretching the lower back and strengthening the core can help prevent pain and improve posture while on the bike.
4. Stretch your hamstrings and quadriceps for better knee function. Cycling puts a lot of strain on the knees, and tight hamstrings and quadriceps can exacerbate this issue. Stretching these muscles can help improve knee function and reduce the risk of injury.
5. Do side bends and spinal rotations to stay flexible overall. Flexibility in the spine is crucial for all physical activities, including cycling. Doing side bends and spinal rotations can help improve overall flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
Remember to hold each stretch for 15-30 seconds without bouncing to avoid injury.
Warm Up Before Going Hard
As with any form of exercise, warming up before cycling is crucial for preventing injury and getting the most out of your ride.
Instead of jumping right into your cycle and pushing yourself to the limit, a dynamic warm-up is recommended as it helps increase your heart rate slowly, allowing your body to adjust to the upcoming activity.

Starting with a moderate speed for at least 5 minutes and gradually increasing the speed over time helps prepare your body for the workout ahead.
Try incorporating some intervals of increased speed to help warm up your muscles and get your blood pumping.
Keep Moving Around Your Body
Maintaining an active posture during cycling is vital to reduce the risk of stiffness and fatigue. You can achieve this by including simple movements during your ride.
Twisting from side to side and rotating the pelvis back and forth are excellent options to alleviate stiffness and prevent fatigue.

Get A Good Saddle
As a cyclist, having a good saddle can make all the difference in your riding experience. Not only can it provide increased comfort, but it can also prevent saddle sores and other genital problems. The right saddle can reduce pressure on your sit bones and improve your overall riding experience.
Visiting a bike retail store is a great way to find the right saddle for you. By trying out different sizes and brands, you can determine what works best for your body type and riding style.
A knowledgeable sales associate can assist you in finding a saddle that is not only comfortable but also optimized for your body’s unique needs.
Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can lead to reduced performance, muscle cramps, and even heat stroke.
For shorter rides, drinking plain water is usually sufficient to keep you hydrated. However, for longer rides, you need to replenish the electrolytes lost through sweat.
Sports drinks can help in this regard, as they contain the necessary electrolytes that plain water may not provide. But, be mindful of the sugar content in sports drinks and opt for low-sugar options or dilute them with water.

It’s crucial to drink regularly, even if you don’t feel thirsty. Waiting until you are thirsty can lead to dehydration, so aim to drink water or a sports drink at least every 15 minutes. On longer rides, aim to drink at least one water bottle per hour of cycling to stay properly hydrated.
It’s also important to remember that individual hydration needs vary based on body weight and temperature, so adjust accordingly. If it’s hot and humid out, you may need to drink more to prevent dehydration.
And, while it may be tempting to reach for coffee or alcohol after a ride, remember that these beverages can dehydrate you. So, make sure to drink plenty of water or a sports drink to rehydrate your body.
Don’t Forget To Cool Down
Cooling down after a workout or physical activity is just as important as warming up before.
Stretching can significantly reduce your chances of injury, by helping your muscles recover from the strain of exercise and restoring their natural range of motion.
A cool-down should consist mostly of static stretching, meaning you stay in one position for at least 30 seconds.
Add Cross Training To The Mix
Cross-training provides an opportunity to break out of a regular workout routine, allowing you to add some variety to your weekly routine and keep your workouts interesting and enjoyable.
The key to successful cross-training is making sure that your activities vary greatly from each other.

For example, if you cycle regularly then it would be beneficial to add some running or strength training into the mix in order to round out your regimen and work all muscle groups effectively.
Swimming is also a great activity for cross-training as it involves full-body movement with minimal risk of injury.
Ensure Proper Bike Fit
Proper bike fit is an essential preventative measure for avoiding cycling injuries. Improper bike fit can cause imbalances and misalignments in the body, leading to discomfort and pain while cycling.
The key components of the bike that should be adjusted include the handlebars, seat, and cleat position.
The handlebars need to be at an appropriate height and angle that allows for a comfortable grip and an upright riding position.

The seat height and position must also be adjusted to avoid knee strain and pressure points. The cleat position should also be adjusted to help distribute pressure evenly across the foot.
Speaking to a specialist at a bike shop is highly recommended for ensuring proper bike fit. These professionals have access to specialized tools and techniques that enable them to fully customize the bike to your body’s proportions, leading to the closest possible fit.
A specialist bike fitting can identify imbalances and areas of pressure that need adjustment, leading to a more comfortable and efficient cycling experience.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, preventing cycling injuries requires a combination of proper equipment, technique, and conditioning.
Always wear a well-fitting helmet and consider using padded shorts and gloves for added comfort.
Focus on maintaining proper form and posture while cycling, and gradually increase mileage and intensity to avoid overuse injuries.
Finally, don’t forget to stretch and cross-train to maintain overall fitness and flexibility. By following these tips, you can enjoy cycling while minimizing your risk of injury.





